The divisions contacts between units are based on color texture or rock composition. For example geologic units usually are listed in order from the youngest most recently formed rock types to the oldest formed earliest in time.
Geologists are trained in map reading and map making.

. On the map itself. Each geologic map has a map key which is a table explaining the meanings of all colors and symbols used to represent geologic features in the map. Often drawn on a topographic base map and have a stratigraphic key showing rock units in a column arranged by geologic age.
A mappable unit of rock or sediment is one that a geologist can consistently recognize trace across a landscape and describe so that other people are able to recognize it and verify its presence and identity. The base map orients the user in space by showing the location of rivers lakes roads hills and valleys. The map in your cars glove compartment doesnt have much on it beyond highways towns shorelines and borders.
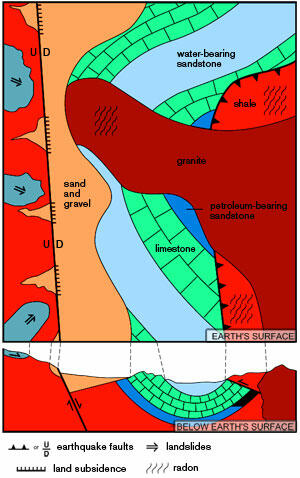
Geologic maps show the distribution of rocks at the Earths surface. Graphic representation of typical information in a general purpose geologic map that can be used to identify geologic hazards locate natural resources and facilitate land-use planning. To play this quiz please finish editing it.
These rock units are known as formations. 22 Questions Show answers. This is because most structures tend to dip or plunge and therefore one can infer the direction and degree of dip or plunge through outcrop patterns.
Geological maps show the distribution of geological features such as rock types and faults. By studying maps a geologist can see the shape and geology of the earths surface and deduce the geological structures that lie hidden beneath the surface. The following images show a base map aerial photo a geologic map and the same map combined with a satellite image to highlight the topography.
Geological Survey uses symbols to indicate the type of roads significant buildings power lines and much more. Maps are as important in geology as written texts are in the study of literature. Geologic map but to create a database from which many types of geologic and engineering geology maps can be derived.
Geologic maps only show what is exposed at the surface of the Earth. Rocks are commonly split into distinguishable rock units that can be traced throughout the map area. Geological map shows locations and types of rocks and other features like faults and folds compass provides direction of north east south and west contact line light thin line that separates rock units or types on a geologic map cartographer someone who creates maps Related questions QUESTION.
This requires a database de-sign or data model that is sufficiently robust to manage complex geologic concepts such as three-dimensional spatial and temporal relations among map units faults and other features Fig. Geologic maps show the outcrop patterns of rock bodies formations and geologic structures faults folds on the land surface. For some areas researchers have compiled geologic map data to create a new geologic map compilation to address basin-scale mountain-block scale or.
They are best known for showing topography either by colors or as shaded relief. Geologic map Click card to see definition These depict the distribution of rock units at Earths surface using colors lines and special symbols see Annex A. Designed to meet South Carolina.
Geologic Map compilations of other scales. Bernknopf et al 1993. Identify and illustrate geologic features of South Carolina and other regions of the world through imagery including aerial.
The geologist usually gathers much of the information shown in a geologic map by examin- ing rock outcrops in the field. Although maps are two-dimensional sheets of paper they portray the geology in three-dimensions. Geologic information is drawn on top of a base map.
Topographic Maps Topographic maps show elevations which is the height of. Scales contour intervals accuracy specifica. They are general overlaid with a base map which is like a normal map so as to help you understand.
Geologic maps in Bulletins Circulars Memoirs and Open-File Reports. Rangle maps produced by the Geological Survey have been designed to be used for many purposes. And yet if you look at it closely you can see how hard it is to fit all that detail on paper so its useful.
The red screen indicates land that is covered with homes. A geologic map depicts the geologists observa- tions and inferences about the surface distribution geometry and structure of the various rocks and sedi- ments in the area. Geologic maps are important for two reasons.
This sample of a 1947 map from the US. Maps are essential tools in geology. This geologic law states that fossils succeed each other vertically in a specific reliable order that can be identified over wide horizontal distances.
The key often will give the name of the each unit as well as the age and a brief. The blue dash-dotted line represents an intermittent stream one that goes dry for part of the year. A geologic map shows mappable rock units mappable sediment units that cover up the rocks and geologic structures such as faults and folds.
Physical maps are designed to show the natural landscape features of Earth. To find a rock formation or group you should probably look. Geologic mapping is a highly interpretive scientific process that can produce a range of map products for many different uses including assessing ground-water.
At the cross sections. Also we use special geologic symbols to indicate 3-dimensionality on our maps. Physical maps often have a green to brown to gray color scheme for showing the elevation of the land.
On the legend of a geologic maps the youngest rocks are found. Geologic maps may be the most concentrated form of knowledge ever put on paper a combination of truth and beauty. Second geologic maps are essential tools for practical applications such as zoning civil engineering and hazard assessment.
Aerial photographs at the same scale as the map which show all features at true scale size small. First as geologists make geologic maps and related explanations and cross-sections they develop a theoretical understanding of the geology and geologic history of a given area. Usually the rocks are divided into mappable units that can be easily recognized and traced across an area.
Geological Survey topographic maps usu. It depends how many rocks there are.
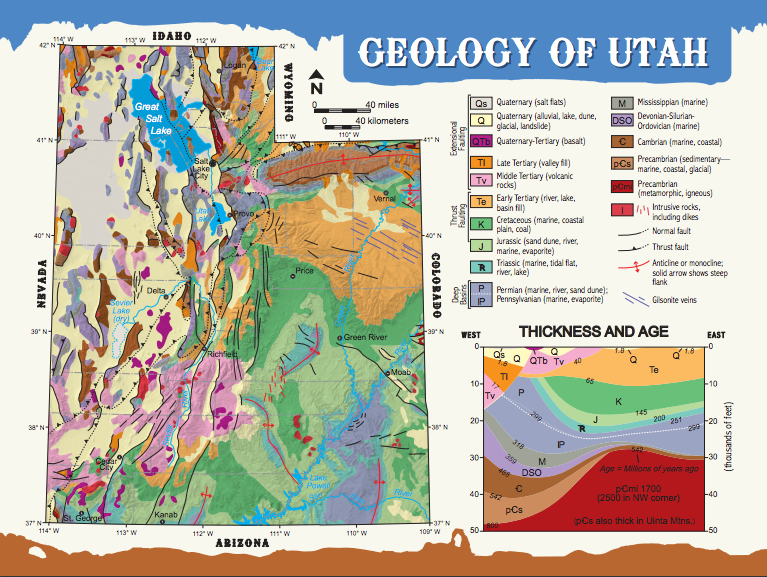
Geologic Maps What Are You Standing On Utah Geological Survey

Section 3 Types Of Maps Preview Objectives Topographic Maps Ppt Download
How Are Maps Used In Science Montana Science Partnership
Cosscience1 Lesson 9 03 Geologic And Topographic Maps

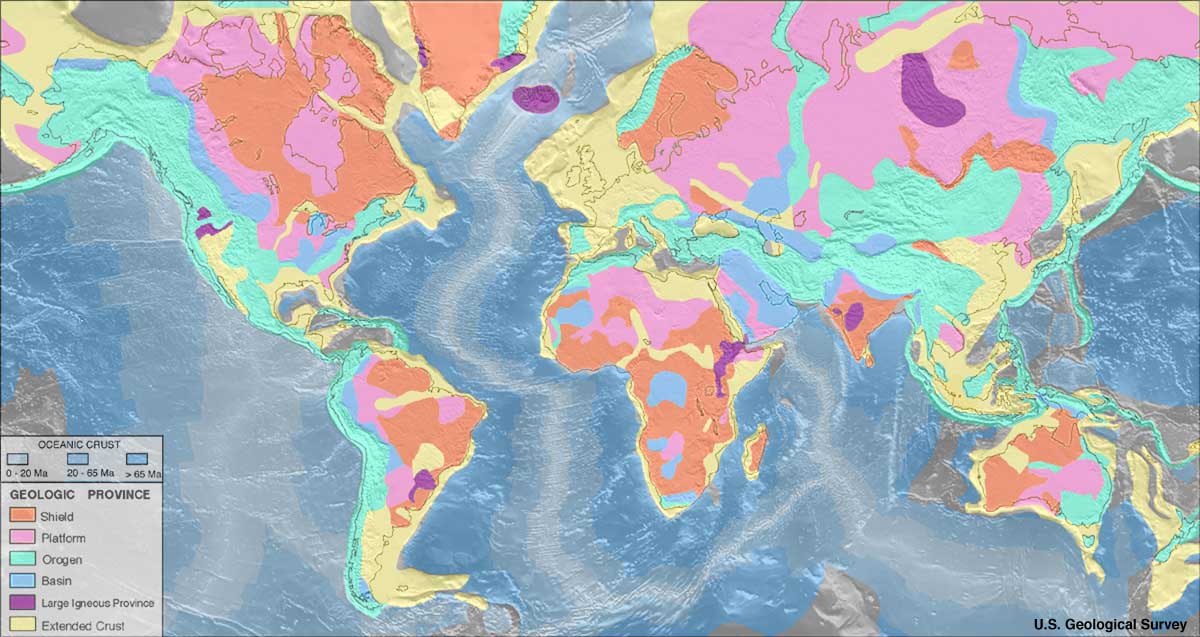
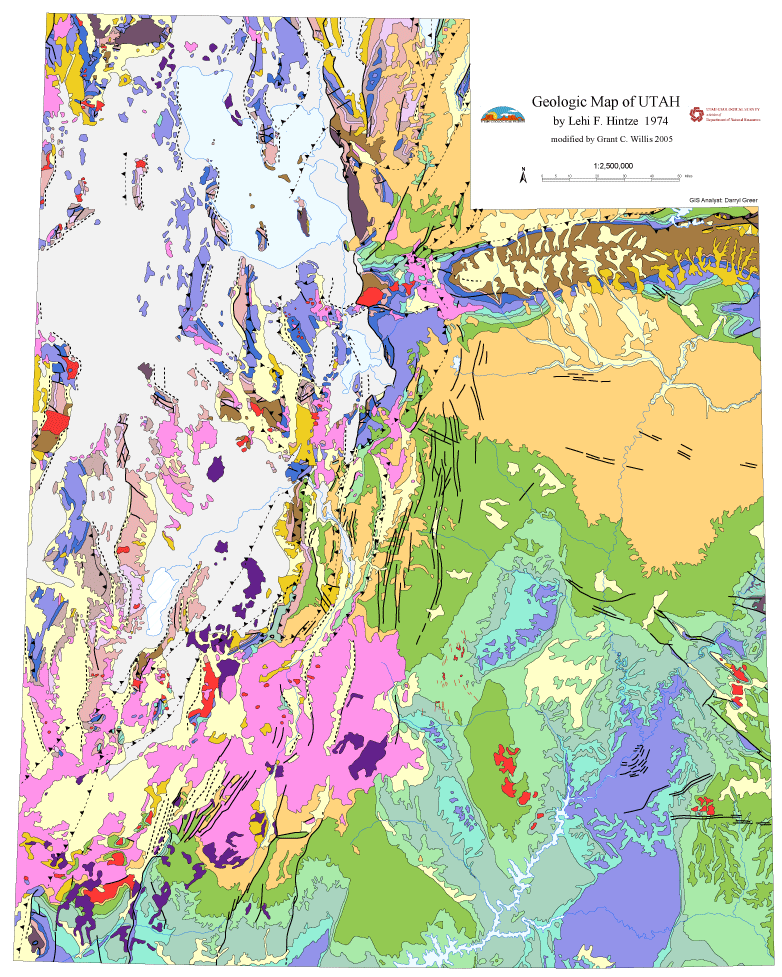
0 comments
Post a Comment